Table of Contents
The Capture app records into C16 files, and the Replay app read those files. (Support for C8 format has since been added to firmware, but this chapter assumes that files were captured in C16 format; most instructions below apply to C8 files as well by just replacing the 16 with 8.)
As described in an issue in PortaPack's repo, this format consist of a tuple of 16 bits signed integers. The first number is I and second Q, forming a complex number. As a result, you get a tridimensional representation of the capture: the real and the imaginary parts in the file (I and Q) versus the time (defined by the sample rate, in this case in an adjacent TXT file with the same filename as the C16).
Capture Manipulation (Audacity)
You can open the C16 file in Audacity importing it as Raw data. Consider the sample rate you used when you did the capture.
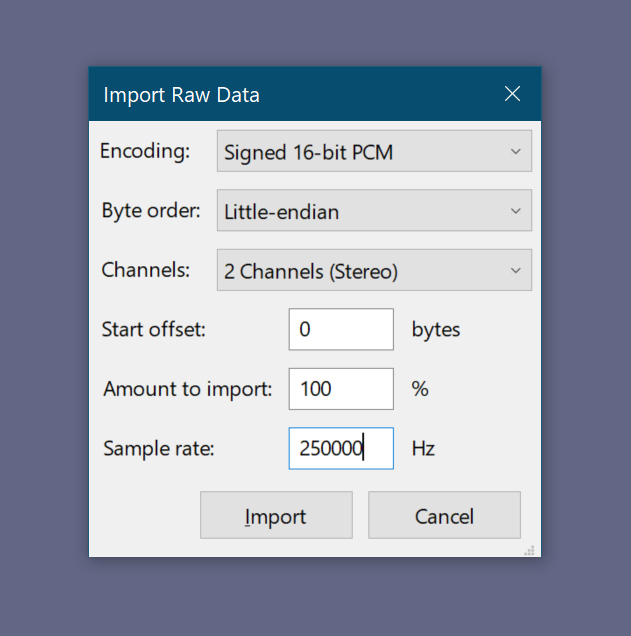
It is possible to manipulate the data as if it was audio. When importing the file as signed 16 bit PCM with two channels, the upper channel contains the I and the second Q, as explained above. You can apply filters, add silences, trim, mix and merge.
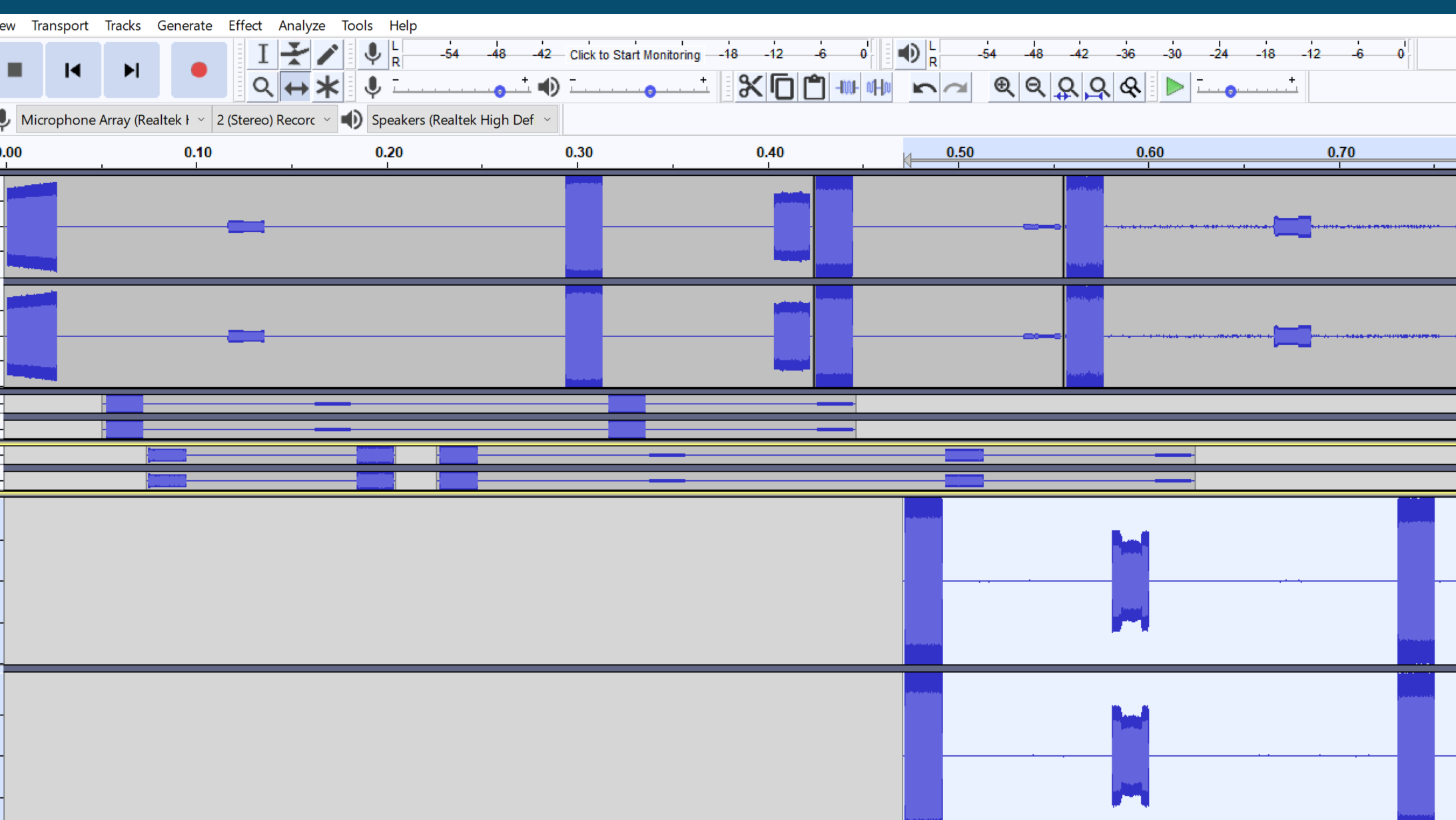
To export the data as a C16 file, select Export, Export Audio ... and then select RAW as a 16 bit signed PCM. After saving, change the extension and you will be able to use the file in the Replay app.
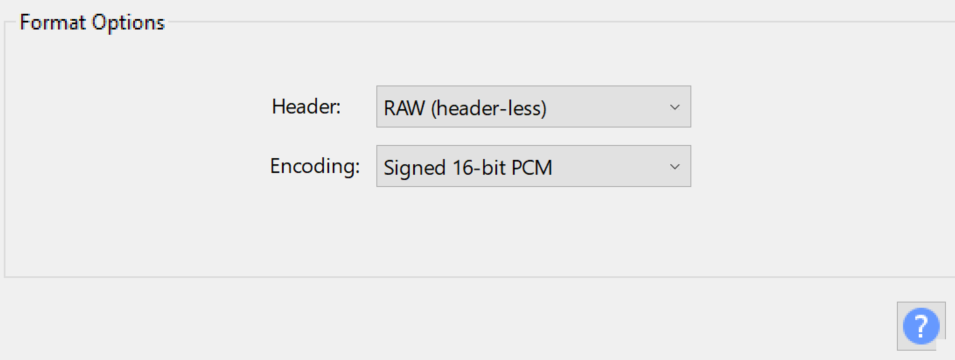
For using the new C16 file in the Replay app, you will also need to include a TXT file with the following metadata (frequency and sample rate):
sample_rate=<RATE IN HZ>
center_frequency=<FREQ IN HZ>
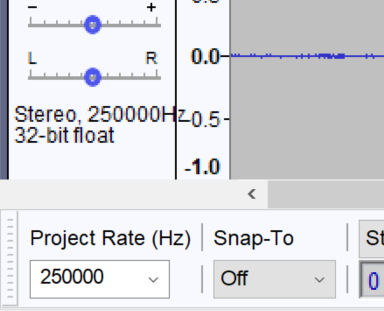
As a final remark, if you created a new file, be sure that the Project Rate matches your capture:
Capture Manipulation (GNU Radio)
You can use GNU Radio Companion (GRC) to convert the C16 short into a complex IQ file.
As seen in the image above you'll need to bring in the original C16 file using the GRC block File Source setting the output type to short, pipe it to IShort To Complex, then Multiply Constant using the magic number 1.0 / 32768.0 for the constant, and finally export it with File Sink.
The reason that the value 32768.0 is used to normalize the C16 capture is because int16 has a range of -32768 to +32767. 2^15 is 32768.0, so dividing int16 value by 2^15 gives a number that is normalized between -1 and +1.
This GRC script can be found at firmware/tools/convert_C16_to_complex.grc
This file contains Unicode characters that might be confused with other characters. If you think that this is intentional, you can safely ignore this warning. Use the Escape button to reveal them.
How to collaborate
How to ask questions correctly
User manual
- First steps
- Usage cautions
- Intended use and Legality
- Features
- PortaPack Versions (which one to buy)
- HackRF Versions
- Firmware update procedure
- Description of the hardware
- User interface
- Powering the PortaPack
- Troubleshooting
- Won't boot
- Config Menu
- Firmware upgrade
- Diagnose firmware update in Windows
- Receive Quality Issues
- No TX/RX
- TX Carrier Only
- H2+ speaker modifications
- Dead Coin Cell Battery
- Factory Defaults
- SD card not recognized by PC with the SD-card over USB selected
- DFU overlay
- Full reset
- SolveBoard
- How to Format SDCard
- What if I don't like some of the apps
- Applications
Misc
Developer Manual
- Compilation of the firmware
- Compile on WSL with ninja
- How to compile on Windows faster with WSL 2
- Using Docker and Kitematic
- Docker command-line reference
- Using Buddyworks and other CI platforms
- Notes for Buddy.Works (and other CI platforms)
- Using ARM on Debian host
- All in one script for ARM on Debian host
- Compile on Arch based distro (exclude Asahi)
- Dev build versions
- Notes About ccache
- Create a custom map
- Code formatting
- PR process
- Description of the Structure
- Software Dev Guides
- Tools
- Research
- UI Screenshots
- Maintaining
- Creating a prod/stable release (Maintainers only)
- Maintaining rules
- Development States Notes
Hardware Hacks
Note
The wiki is incomplete. Please add content and collaborate.
Important
- This is a public wiki. Everything is visible to everyone. Don't use it for personal notes.
- Avoid linking to external tutorials/articles; they may become outdated or contain false information.
